AIM: To find the ductility value of the given bituminous material
APPARATUS:
The ductility test apparatus consists of items like sample (briquette) moulds, water bath square-end trowel or putty knife sharpened on end and ductility machine.
Briquette mould: Mould is made of brass metal with shape and dimensions as indicated. Both ends called clips posses circular holes to grip the fixed and movable ends of the testing machine. Side pieces when placed together form the briquette of the following dimensions:
Length : 75 mm
Distance between clips : 30 mm
Width at mouth of clips : 20 mm Cross section at minimum width : 10 x 10 mm
Ductility machine: It is equipment which functions as constant temperature water bath and a pulling device at a pre-calibrated rate. The central rod of the machine is threaded and through a gear system provides movement to one end where the clip is fixed during initial placement. The other clip end is hooked at the fixed end of the machine. Two clips are thus pulled apart horizontally at a uniform speed of 50 ± 2.5 mm per minute. The machine may have provision to fix two or more mould so as to test these specimens simultaneously.
PROCEDURE:
The bitumen sample is melted to a temperature of 750 C to 1000 C above the approximate softening point until it is fluid. It is strained through IS sieve 30, poured in the mould assembly and placed on a brass plate, after a solution of glycerin and dextrin is applied at all surfaces of the mould exposed to bitumen.
Thirty to forty minutes after the sample is poured into the moulds, the plate assembly along with the sample is placed in water bath maintained at 270 C for 30 minutes. The sample and mould assembly is removed from water bath and leveling the surface using hot knife cuts off excess bitumen material. After trimming the specimen, the mould assembly-containing sample is replaced in water bath maintained at 270 C for 85 to 90 minutes. The sides of the mould are now removed and the clips are carefully booked on the machine without causing any initial strain. Two or more specimens may be prepared in the moulds and clipped to the machine so as to conduct these tests simultaneously.
The pointer is set to read zero. The machine is started and the two clips are thus pulled apart horizontally. While the test is in operation, it is checked whether the sample is immersed in water at depth of at least 10 mm. The distance at which the bitumen thread of each specimen breaks, is recorded (in cm) to report as ductility value.
RESULT
The distance stretched by the moving end of the specimen up to the point of breaking of thread measured in centimeters is recorded as ductility value.
APPLICATIONS OF DUCTILITY TEST
A certain minimum ductility is necessary for a bitumen binder. This is because of the temperature changes in the bituminous mixes and the repeated deformations that occur in flexible, pavements due to the traffic loads. If the bitumen has low ductility value, the bituminous pavement may crack, especially is cold weather. The ductility values of bitumen vary from 5 to over 100. Several agencies have specified the minimum ductility for various types of bituminous pavement. Often a minimum ductility value of 50 cm is specified for bituminous construction.
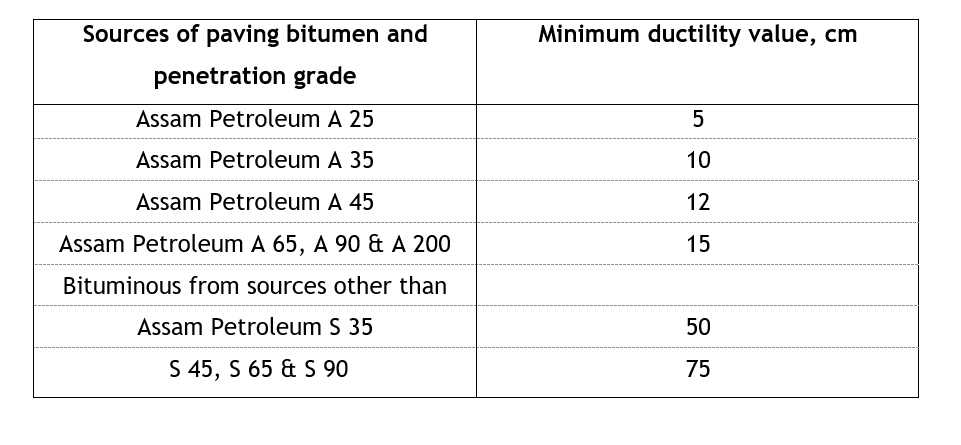
The minimum ductility values specified by the Indian Standards Institutions for various grades bitumen available in India are given below:
APPARATUS:
The ductility test apparatus consists of items like sample (briquette) moulds, water bath square-end trowel or putty knife sharpened on end and ductility machine.
Briquette mould: Mould is made of brass metal with shape and dimensions as indicated. Both ends called clips posses circular holes to grip the fixed and movable ends of the testing machine. Side pieces when placed together form the briquette of the following dimensions:
Length : 75 mm
Distance between clips : 30 mm
Width at mouth of clips : 20 mm Cross section at minimum width : 10 x 10 mm
Ductility machine: It is equipment which functions as constant temperature water bath and a pulling device at a pre-calibrated rate. The central rod of the machine is threaded and through a gear system provides movement to one end where the clip is fixed during initial placement. The other clip end is hooked at the fixed end of the machine. Two clips are thus pulled apart horizontally at a uniform speed of 50 ± 2.5 mm per minute. The machine may have provision to fix two or more mould so as to test these specimens simultaneously.
PROCEDURE:
The bitumen sample is melted to a temperature of 750 C to 1000 C above the approximate softening point until it is fluid. It is strained through IS sieve 30, poured in the mould assembly and placed on a brass plate, after a solution of glycerin and dextrin is applied at all surfaces of the mould exposed to bitumen.
Thirty to forty minutes after the sample is poured into the moulds, the plate assembly along with the sample is placed in water bath maintained at 270 C for 30 minutes. The sample and mould assembly is removed from water bath and leveling the surface using hot knife cuts off excess bitumen material. After trimming the specimen, the mould assembly-containing sample is replaced in water bath maintained at 270 C for 85 to 90 minutes. The sides of the mould are now removed and the clips are carefully booked on the machine without causing any initial strain. Two or more specimens may be prepared in the moulds and clipped to the machine so as to conduct these tests simultaneously.
The pointer is set to read zero. The machine is started and the two clips are thus pulled apart horizontally. While the test is in operation, it is checked whether the sample is immersed in water at depth of at least 10 mm. The distance at which the bitumen thread of each specimen breaks, is recorded (in cm) to report as ductility value.
RESULT
The distance stretched by the moving end of the specimen up to the point of breaking of thread measured in centimeters is recorded as ductility value.
APPLICATIONS OF DUCTILITY TEST
A certain minimum ductility is necessary for a bitumen binder. This is because of the temperature changes in the bituminous mixes and the repeated deformations that occur in flexible, pavements due to the traffic loads. If the bitumen has low ductility value, the bituminous pavement may crack, especially is cold weather. The ductility values of bitumen vary from 5 to over 100. Several agencies have specified the minimum ductility for various types of bituminous pavement. Often a minimum ductility value of 50 cm is specified for bituminous construction.
The minimum ductility values specified by the Indian Standards Institutions for various grades bitumen available in India are given below:

