STIFFNESS MATRIX METHOD
1. What are the basic unknowns in stiffness matrix method?
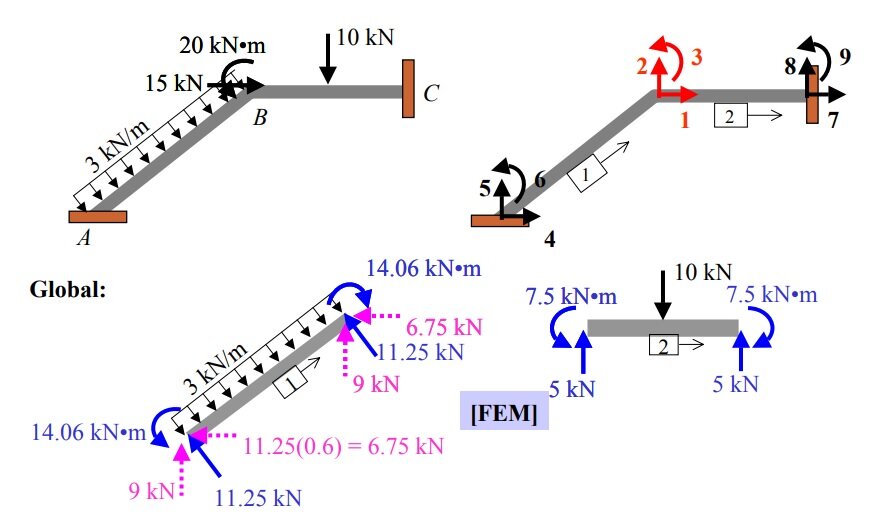
In the stiffness matrix method nodal displacements are treated as the basic unknowns for the solution of indeterminate structures.
2. Define stiffness coefficient kij.
Stiffness coefficient 'kij' is defined as the force developed at joint 'i' due to unit displacement at joint 'j' while all other joints are fixed.
3. What is the basic aim of the stiffness method?
The aim of the stiffness method is to evaluate the values of generalized coor dinates 'r' knowing the structure stiffness matrix 'k' and nodal loads 'R' through the structure equilibrium equation.
{R} =[K]{r}
4. What is the displacement transformation matrix?
The connectivity matrix which relates the internal displacement 'q' and the external displacement 'r' is known as the displacement transformation matrix 'a'.
{q} =[a]{r}
5. How are the basic equations of stiffness matrix obtained?
The basic equations of stiffness matrix are obtained as:
Equilibrium forces
Compatibility of displacements
Force displacement relationships
6. What is the equilibrium condition used in the stiffness method?
The external loads and the internal member forces must be in equilibrium at the nodal points.
7. What is meant by generalized coordinates?
For specifying a configuration of a system, a certain minimum no of indepen dent coordinates are necessary. The least no of independent coordinates that are needed to specify the configuration is known as generalized coordinates.
8. What is the compatibility condition used in the flexibility method?
The deformed elements fit together at nodal points.
9. Write about the force displacement relationship.
The relationship of each element must satisfy the stress-strain relationship of the element material.
1. What are the basic unknowns in stiffness matrix method?
In the stiffness matrix method nodal displacements are treated as the basic unknowns for the solution of indeterminate structures.

2. Define stiffness coefficient kij.
Stiffness coefficient 'kij' is defined as the force developed at joint 'i' due to unit displacement at joint 'j' while all other joints are fixed.
3. What is the basic aim of the stiffness method?
The aim of the stiffness method is to evaluate the values of generalized coor dinates 'r' knowing the structure stiffness matrix 'k' and nodal loads 'R' through the structure equilibrium equation.
{R} =[K]{r}
4. What is the displacement transformation matrix?
The connectivity matrix which relates the internal displacement 'q' and the external displacement 'r' is known as the displacement transformation matrix 'a'.
{q} =[a]{r}
5. How are the basic equations of stiffness matrix obtained?
The basic equations of stiffness matrix are obtained as:
Equilibrium forces
Compatibility of displacements
Force displacement relationships
6. What is the equilibrium condition used in the stiffness method?
The external loads and the internal member forces must be in equilibrium at the nodal points.
7. What is meant by generalized coordinates?
For specifying a configuration of a system, a certain minimum no of indepen dent coordinates are necessary. The least no of independent coordinates that are needed to specify the configuration is known as generalized coordinates.
8. What is the compatibility condition used in the flexibility method?
The deformed elements fit together at nodal points.
9. Write about the force displacement relationship.
The relationship of each element must satisfy the stress-strain relationship of the element material.
