BULKING OF SAND by LAB. METHOD
AIM: To ascertain the bulking Phenomena of given sample of sand. APPARATUS: Special Vessel for unit volume, tray, balance and weights, THEORY:
Increase in volume of sand due to presence of moisture is known as Bulking of sand. Bulking is due to the formation of thin film of water around the sand grains and the interlocking of air in between the sand grains and the film of water. When more water is added a sand particles got submerged and volume again becomes equal to dry volume of sand. To compensate the bulking effect extra sand is added in the concrete so that the ration of coarse to fine aggregate will not change from the specified value. Fine sands shown greater percentage of bulking than coarse sands with equal percentage of moisture.
PROCEDURE:
Compact the sand in three layers in the vessel, each layer being given 25 strokes, and strike level at top. Weigh it and dump it into a tray. Add a certain percent of water by weight (say 2%) of dry compacted tray. Add a certain percent of water by weight (say 2%) of dry compacted sand. Mix, well till uniformly moist. Fill the container with the wet sand without any tamping strike tip surface level, and find weight of the wet loose sand.
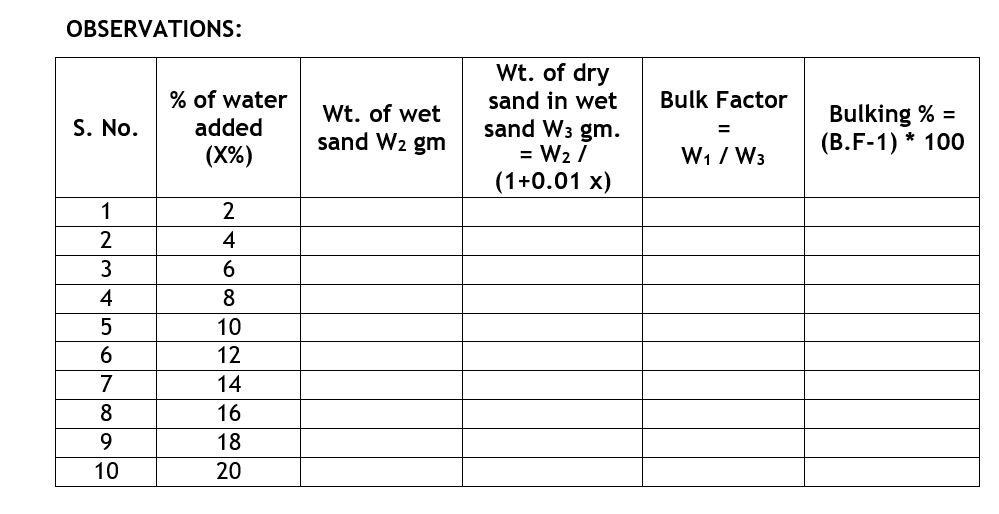
CALCULATIONS:
Weight of unit volume of dry compacted sand = W1 Weight of loose wet sand of unit volume = W2
If moisture content be x% in sand, and if W3 is weight of dry sand in W2 of loose wet sand,
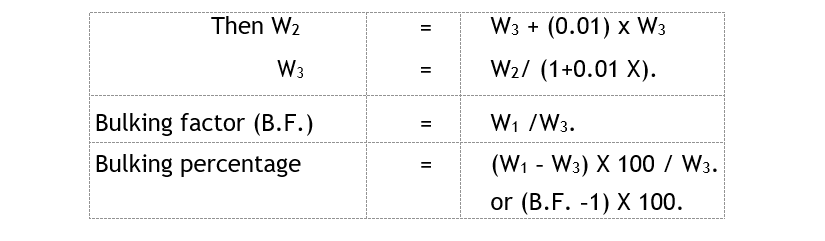
GRAPH: Plot graph between B.F. on (Y- axis) and water content on (X- axis).
RESULT:
AIM: To ascertain the bulking Phenomena of given sample of sand. APPARATUS: Special Vessel for unit volume, tray, balance and weights, THEORY:
Increase in volume of sand due to presence of moisture is known as Bulking of sand. Bulking is due to the formation of thin film of water around the sand grains and the interlocking of air in between the sand grains and the film of water. When more water is added a sand particles got submerged and volume again becomes equal to dry volume of sand. To compensate the bulking effect extra sand is added in the concrete so that the ration of coarse to fine aggregate will not change from the specified value. Fine sands shown greater percentage of bulking than coarse sands with equal percentage of moisture.
PROCEDURE:
Compact the sand in three layers in the vessel, each layer being given 25 strokes, and strike level at top. Weigh it and dump it into a tray. Add a certain percent of water by weight (say 2%) of dry compacted tray. Add a certain percent of water by weight (say 2%) of dry compacted sand. Mix, well till uniformly moist. Fill the container with the wet sand without any tamping strike tip surface level, and find weight of the wet loose sand.
CALCULATIONS:
Weight of unit volume of dry compacted sand = W1 Weight of loose wet sand of unit volume = W2
If moisture content be x% in sand, and if W3 is weight of dry sand in W2 of loose wet sand,
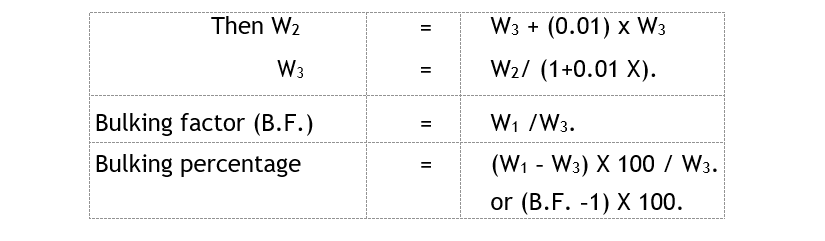
GRAPH: Plot graph between B.F. on (Y- axis) and water content on (X- axis).
RESULT:
- Moisture content at maximum bulking =
- Percentage of maximum bulking =