AIM: To find the Los Angeles abrasion value of given aggregate sample
APPARATUS: The apparatus consists of Los Angeles machine, abrasive charge and sieves.
Los Angeles machine consists of a hollow steel cylinder, closed at both ends, having an inside diameter 70cm and an inside length of 50 cm, mounted on stub shafts about which it rotates on a horizontal axis.
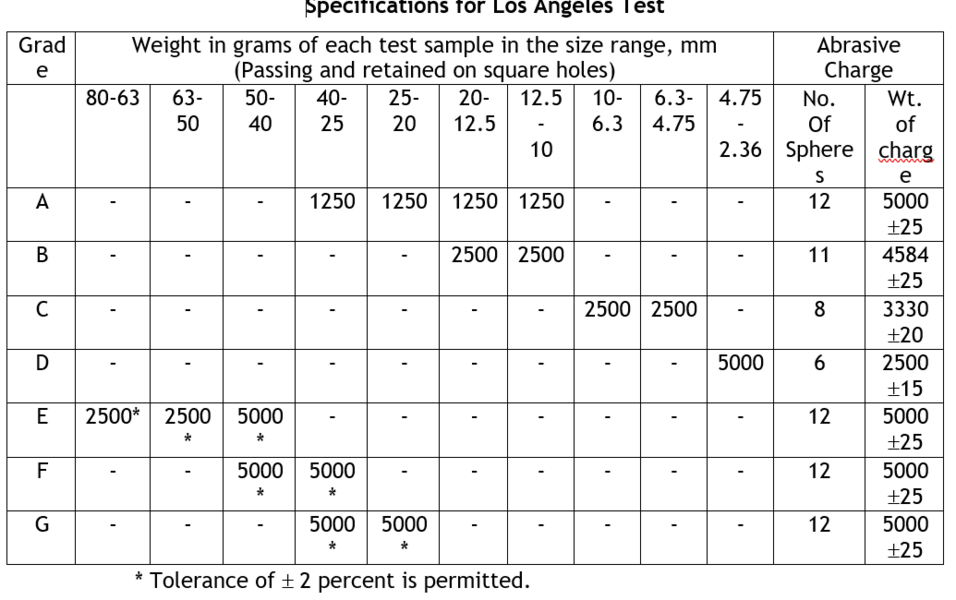
An opening is provided in the cylinder for the introduction of the test sample. A removable cover of the opening is provided in such a way that when closed and fixed by bolts and nut, it is dust-tight and the interior surface is perfectly cylindrical. A removable steel shelf projecting radial 8.8 cm into the parallel to the axis. The shelf is fixed at a distance of 12.5 cm from the opening, measured along the circumference in the direction of rotation. Abrasive charge, consisting of cast iron spheres approximately 4.8 cm in diameter and 390 to 445 g in weight are used. The weight of the sphere of the aggregates tested. The aggregates grading have been standardized as A, B, C, D, E, F and G for this test and the IS specifications for the grading and abrasive charge to be used are given in Table
IS sieve with 1.70 mm opening is used for separating the fines after the abrasion test.
PROCEDURE:
Clean aggregates dried in an oven at 105-1100 C to constant weight, conforming to any one of the grading A to G, as per Table 11.1 is used for the test. The grading or grading’s used in the test should be nearest to the grading to be used in the construction. Aggregates weighing 5 kg for grading A, B, C or D and 10 kg for grading E, F or G may be taken as test specimen and placed in the cylinder. The abrasive charge is also chosen in accordance with Table 1 depending on the grading of the aggregate and is placed in the cylinder of the machine. The cover is then fixed dust-tight. The machine is rotated at a speed of 30 to 33 revolutions per minute. The machine is rotated for 500 revolutions for grading A, B, C and D, for grading’s E, F and G, it shall be rotated for 1,000 revolutions. The machine should be balanced and driven in such a way as to maintain uniform peripheral speed.
After the desired number of revolutions, the machine is stopped and the material is discharged from the machine taking care to take out entire stone dust. Using a sieve of size larger than 1.70 mm IS sieve, 1.7 mm IS sieve. The portion of material coarser than 1.7 mm size is washed and dried in an oven at 105 to 1100 C to constant weight and weighed correct to one gram.
CALCULATIONS
The difference between the original and final weights of the sample is expressed as a percentage of the original weight of the sample is reported as the percentage wear.
Let the original weight of aggregate = W1 g
Weight of aggregate retained on 1.70 mm IS sieve after the test = W2 g
Loss in weight due to wear = (W1-W2) g
Los Angeles abrasion value, % = Percentage wear = (W1-W2) x 100W1
RESULT:
The result of the Los Angeles abrasion test is expressed as a percentage wear and the average value of two tests may be adopted as the Los Angeles abrasion value.
INTERFERENCE:
Los Angeles Abrasion Test is very widely accepted as a suitable test to assess the hardness of aggregates used in pavement construction. Many agencies have specified the desirable limits of the test, for different methods of pavement construction. The maximum allowable Los Angeles abrasion values of aggregates as specified by Indian Roads Congress for different methods of construction are Given in Table 1.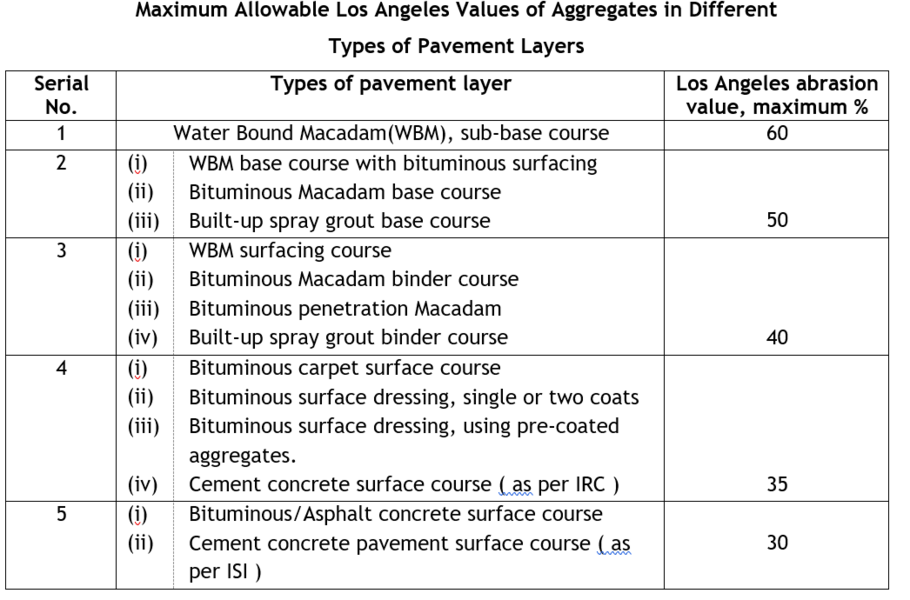
APPARATUS: The apparatus consists of Los Angeles machine, abrasive charge and sieves.
Los Angeles machine consists of a hollow steel cylinder, closed at both ends, having an inside diameter 70cm and an inside length of 50 cm, mounted on stub shafts about which it rotates on a horizontal axis.
An opening is provided in the cylinder for the introduction of the test sample. A removable cover of the opening is provided in such a way that when closed and fixed by bolts and nut, it is dust-tight and the interior surface is perfectly cylindrical. A removable steel shelf projecting radial 8.8 cm into the parallel to the axis. The shelf is fixed at a distance of 12.5 cm from the opening, measured along the circumference in the direction of rotation. Abrasive charge, consisting of cast iron spheres approximately 4.8 cm in diameter and 390 to 445 g in weight are used. The weight of the sphere of the aggregates tested. The aggregates grading have been standardized as A, B, C, D, E, F and G for this test and the IS specifications for the grading and abrasive charge to be used are given in Table
IS sieve with 1.70 mm opening is used for separating the fines after the abrasion test.
PROCEDURE:
Clean aggregates dried in an oven at 105-1100 C to constant weight, conforming to any one of the grading A to G, as per Table 11.1 is used for the test. The grading or grading’s used in the test should be nearest to the grading to be used in the construction. Aggregates weighing 5 kg for grading A, B, C or D and 10 kg for grading E, F or G may be taken as test specimen and placed in the cylinder. The abrasive charge is also chosen in accordance with Table 1 depending on the grading of the aggregate and is placed in the cylinder of the machine. The cover is then fixed dust-tight. The machine is rotated at a speed of 30 to 33 revolutions per minute. The machine is rotated for 500 revolutions for grading A, B, C and D, for grading’s E, F and G, it shall be rotated for 1,000 revolutions. The machine should be balanced and driven in such a way as to maintain uniform peripheral speed.
After the desired number of revolutions, the machine is stopped and the material is discharged from the machine taking care to take out entire stone dust. Using a sieve of size larger than 1.70 mm IS sieve, 1.7 mm IS sieve. The portion of material coarser than 1.7 mm size is washed and dried in an oven at 105 to 1100 C to constant weight and weighed correct to one gram.
CALCULATIONS
The difference between the original and final weights of the sample is expressed as a percentage of the original weight of the sample is reported as the percentage wear.
Let the original weight of aggregate = W1 g
Weight of aggregate retained on 1.70 mm IS sieve after the test = W2 g
Loss in weight due to wear = (W1-W2) g
Los Angeles abrasion value, % = Percentage wear = (W1-W2) x 100W1

RESULT:
The result of the Los Angeles abrasion test is expressed as a percentage wear and the average value of two tests may be adopted as the Los Angeles abrasion value.
INTERFERENCE:
Los Angeles Abrasion Test is very widely accepted as a suitable test to assess the hardness of aggregates used in pavement construction. Many agencies have specified the desirable limits of the test, for different methods of pavement construction. The maximum allowable Los Angeles abrasion values of aggregates as specified by Indian Roads Congress for different methods of construction are Given in Table 1.

