Index
Introduction
Concrete is still the building block material throughout India, giving strength and solidity to houses, commercial enterprises, and infrastructural developments. Be it a country road in Madhya Pradesh, a metro terminus in Gujarat, or an apartment complex in Delhi, there is one thing that is uniform—the demand for the right concrete mix ratio.
The hardness, durability, and lifespan of a building are highly reliant on the proportion of the concrete used. Concrete mix ratios in India, incorporating grades, application, regional use, and on-site best practices.
These ratios are crucial in obtaining the desired compressive strength and workability of concrete. A disproportionate mix will result in lower durability, higher permeability, and structural failure in the long term.
For instance:
b) Design Mix Concrete
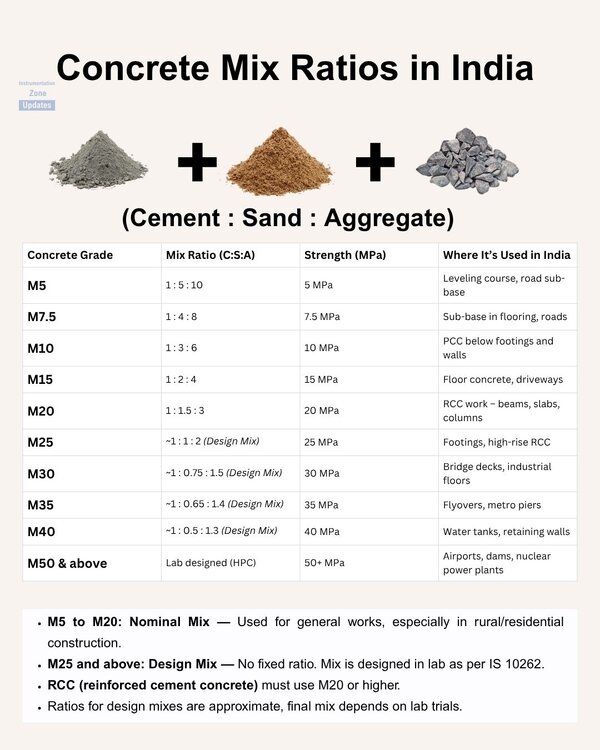
Concrete Grade C:S:A (Cement | Sand | Aggregate)
M5 1:5:10
M7.5 1:4:8
M10 1:3:6
M15 1:2:4
M20 1:1.5:3
M25+ | Design mix – no fixed ratio|
Most contractors nowadays depend on concrete testing equipment, such as cube moulds, compression test machines, and computerized batching units, to check mix quality on site. These instruments, available with a host of professional suppliers in India, are instrumental in providing safety and quality.
Knowing the concrete mix ratio in India is not just important for a civil engineer working on a site but also for a project manager or even a new builder. Understanding what is M25 grade of concrete, nominal mix vs design mix, and how to use concrete grade and their applications makes better decisions possible on the site.
With India developing infrastructure, particularly in areas such as Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, the need for precise and performance-oriented concrete mixing will only continue to increase. By selecting the correct grade and utilizing best practices, engineers and construction workers can build structures that will be remembered for generations.
- Introduction
- What is a Concrete Mix Ratio?
- Understanding M Grades: What is M25 Grade of Concrete?
- Nominal Mix vs Design Mix
- Common Concrete Grades Used in India
- Concrete Mix Ratio Table (Cement:Sand:Aggregate)
- Applications of Various Grades – Regional Examples
- Importance of Choosing the Right Mix
- Best Practices for Mixing Concrete on Site
- Conclusion
Introduction
Concrete is still the building block material throughout India, giving strength and solidity to houses, commercial enterprises, and infrastructural developments. Be it a country road in Madhya Pradesh, a metro terminus in Gujarat, or an apartment complex in Delhi, there is one thing that is uniform—the demand for the right concrete mix ratio.
The hardness, durability, and lifespan of a building are highly reliant on the proportion of the concrete used. Concrete mix ratios in India, incorporating grades, application, regional use, and on-site best practices.
What is a Concrete Mix Ratio?
A mix ratio of concrete is the ratio of cement : sand : aggregate in a mix of concrete. A ratio of 1:2:4 means 1 part cement, 2 parts fine aggregate (sand), and 4 parts coarse aggregate (stone chips).These ratios are crucial in obtaining the desired compressive strength and workability of concrete. A disproportionate mix will result in lower durability, higher permeability, and structural failure in the long term.
M Grades: What is M25 Grade of Concrete?
Indian concrete is graded by the "M" grade system, in which "M" means Mix and the number represents the typical compressive strength in megapascals (MPa) after 28 days of curing.For instance:
- M25 denotes the concrete will be able to resist 25 MPa pressure after 28 days.
- M20 suggests 20 MPa strength, etc.
Nominal Mix Concrete vs Design Mix Concrete
Concrete mix types are broadly classified as:a) Nominal Mix Concrete
- For ordinary, less complex structures
- Contain fixed ratios (e.g., 1:2:4 for M15)
- Grades: M5, M7.5, M10, M15, M20
- Used in house construction and low-rise structures
b) Design Mix Concrete
- Made in a laboratory by testing the material
- Altered according to particular structural and environmental requirements
- Grades: M25 and higher (M30, M35, M40, M50, M60)
- Applied in high-performance structures such as flyovers, bridges, and industry foundations
Common Concrete Grades Used in India
Following is a list of commonly employed concrete grades in India along with their usual applications:
Concrete Mix Ratio Table (Cement:Sand:Aggregate)
Following is a ready reference table indicating cement sand aggregate proportion in India for nominal mixes:Concrete Grade C:S:A (Cement | Sand | Aggregate)
M5 1:5:10
M7.5 1:4:8
M10 1:3:6
M15 1:2:4
M20 1:1.5:3
M25+ | Design mix – no fixed ratio|
Applications of Various Grades – Regional Examples
India's construction requirements differ greatly state by state. This is the way concrete grades are being utilized regionally:- Delhi NCR: M20 and M25 in RCC for residential towers; M30–M40 is prevalent in metro and expressway constructions.
- Madhya Pradesh: M10–M20 for government rural housing projects; M35+ for bridge foundations over rivers such as Narmada.
- Gujarat: M25–M50 grades in smart city and commercial tower schemes in Ahmedabad and Surat; M60+ in BRTS, metro rails, and airports.
Significance of Right Mix Selection
Proper selection of mix ratio ensures:- As desired strength and load carrying capacity
- Proper workability and setting time
- Resistance to cracking and weather effects
- Durability in the long term
Most contractors nowadays depend on concrete testing equipment, such as cube moulds, compression test machines, and computerized batching units, to check mix quality on site. These instruments, available with a host of professional suppliers in India, are instrumental in providing safety and quality.
Best Practices for Site-Mixing Concrete
In order to achieve efficient concrete performance, the following best practices must be observed:- Employ clean graded sand and aggregate
- Ensure a correct water-cement ratio (typically between 0.4 and 0.6)
- Use standard boxes or batching equipment to measure material
- Employ mechanical mixers for uniformity of mixes
- Conduct a slump test to monitor workability
- Cure the concrete for a minimum of 7 to 14 days
Knowing the concrete mix ratio in India is not just important for a civil engineer working on a site but also for a project manager or even a new builder. Understanding what is M25 grade of concrete, nominal mix vs design mix, and how to use concrete grade and their applications makes better decisions possible on the site.
With India developing infrastructure, particularly in areas such as Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and Gujarat, the need for precise and performance-oriented concrete mixing will only continue to increase. By selecting the correct grade and utilizing best practices, engineers and construction workers can build structures that will be remembered for generations.
