Dry Density of soil by Rapid Moisture Meter test
When we want a dry density of soil which are compacted in place, first thing we need to know is current moisture / water content in compacted earth.
We relate the achieved density of soil directly with the moisture / water content in it by comparing with its Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture content.
When we send the sample of soil in lab for determination of MDD and OMC, they do test it with different combination of moisture in proctor test and plot a graph which shows the behavior of soil under different moisture levels. From this graph we get the optimum level of moisture at which the soil can attain maximum dry density.
Once we know the properties of soil, it’s very easy to calculate the dry density of soil by relating it to optimum moisture content.
Calculation of dry density of soil involves measuring of its bulk density and finding moisture content of it. There are many methods available for determination of moisture content in soil.
By oven drying – it takes minimum 24 hours and results are very accurate and precise. Due to time it takes, its avoided in places where quick results are required to progress work at faster rates.
Sand Bath method – Results are not much accurate and required heating of sample.
Alcohol Method – same as sand bath method, need to add Methylated spirit in soil sample and then firing sample to make it dry.
Rapid Moisture test by Infrared lamp and torsion balance – it’s easy to do but required electricity for doing this test, so not feasible in remote places or when site area is big and do not have electricity connection (such as a long road construction).
Rapid Moisture meter – Mostly used at all type of projects and specially in Road constructions, involves less risk and time and produces almost accurate results.
Determination of Moisture content by Rapid moisture meter is easier and requires;
Rapid Moisture Meter
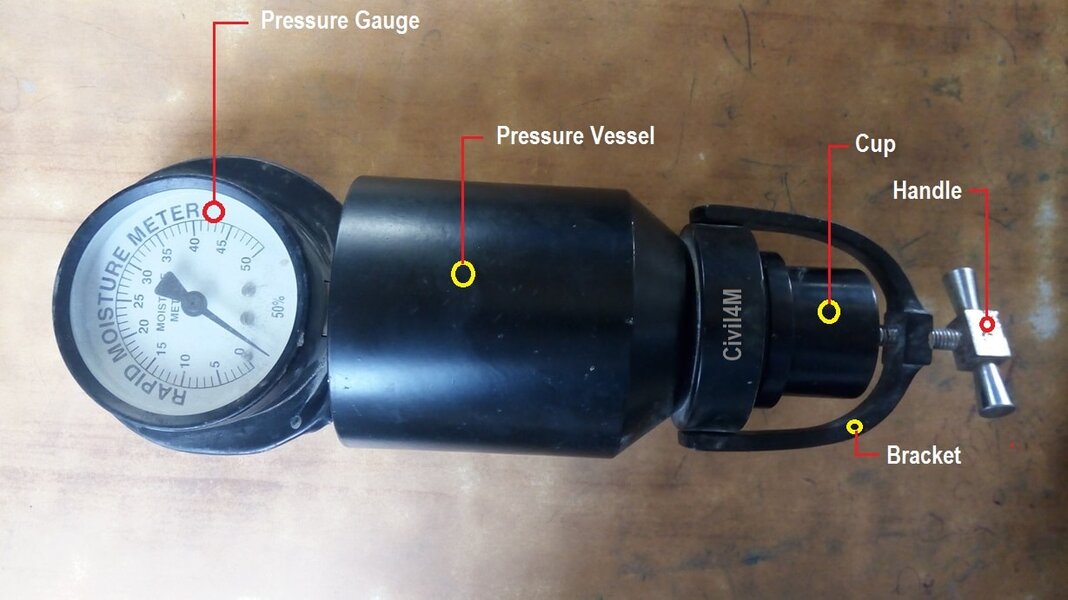

It consists of Pressure gauge, pressure vessel, cup for sample, spherical steel balls, bracket to hold it and handle to fix cup in pressure vessel mouth.
Pressure vessel and cup outer body is made up of aluminium alloy, cup inside is of stainless steel, bracket of copper alloy and handle of mild steel.
Counterpoised balance
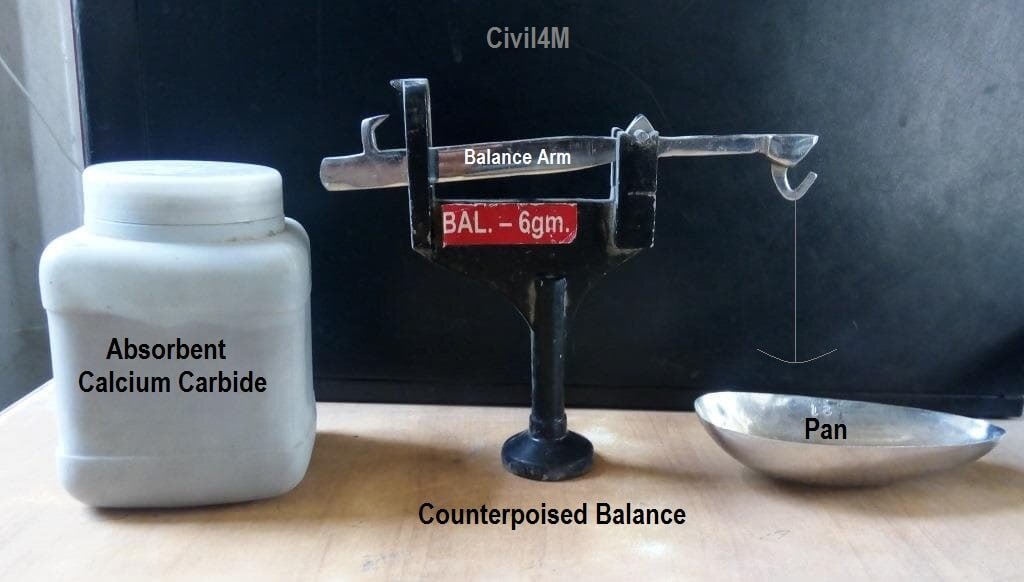
It consists of a stand, balance arm to take exactly 6-gram sample, pan to put sample and stirrup to tie the pan on arm.
Rapid Moisture Meter determines the percentage of water in soil mass through the gas pressure created by reaction between calcium carbide and water present in the wet soil sample. This percentage water need to be converted to as water content in dry mass of soil sample.
For doing this test, collect the sample from site, and setup the counterpoised balance correctly. Then add soil sample in pan till the mark on the balance arm lines up with the index mark.
Clean the chamber and cup body with wire brush to ensure its completely clean.
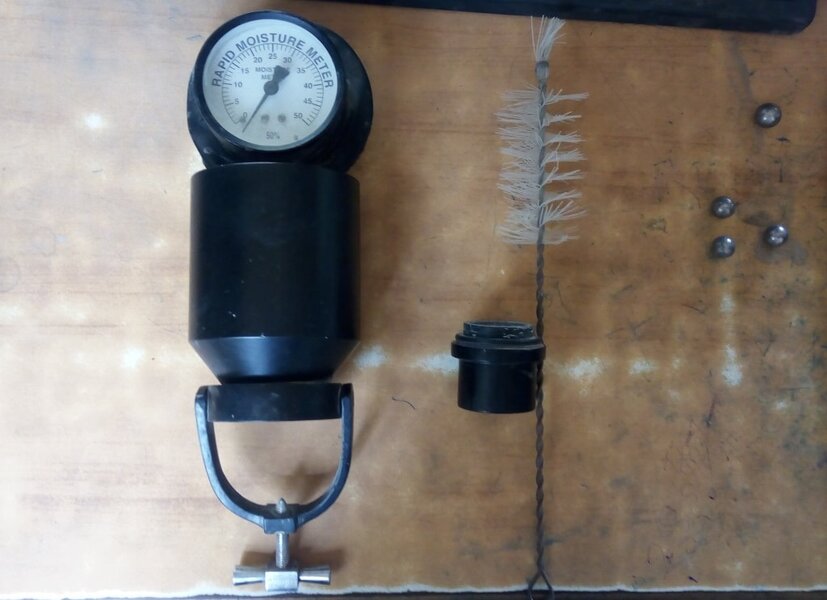

Hold the rapid moisture meter horizontally and gently deposit one level scoopful of calcium carbide halfway inside the chamber. Then lay down the chamber without disturbing it.
Put the weighed sample of soil in cup and keeping cup and chamber horizontal, clamp the cup to chamber.
In case when the sample is bulky, put sample in chamber and calcium carbide in cup.
In case of clayey soils and paste, Place 3 smaller steel balls in cup along with soil sample and large ball in chamber.
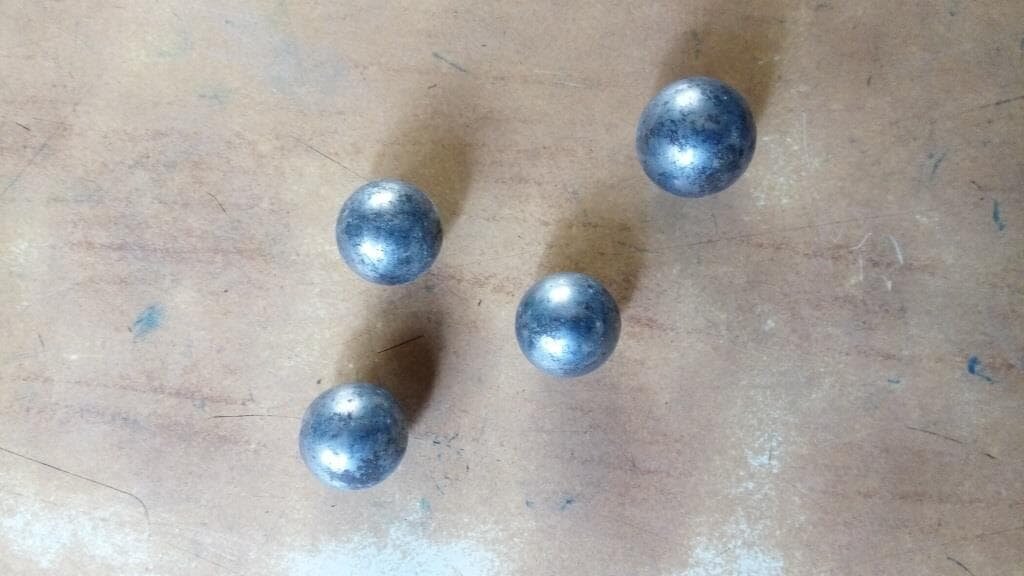

After clamping cup to chamber tightly, with pressure gauge on downward (except when steel balls are used) shake the moisture meter up and down vigorously for 5 seconds and quickly turn it up so that moisture gauge is on upward.
Give the tap on moisture meter body to ensure all content falls in the cup.
Hold the rapid moisture meter gauge downward and shake it for 5 seconds, then turn it up with gauge upward and tap.
Hold for one minute and repeat it third time.
Once more invert the moisture meter and shake it up and down to cool the gas.
Turn the moisture meter gauge upward and hold it at chest level, when needle / pointer come to rest without fluctuations, take the reading as a percentage of moisture/ water in wet sample of soil.
In case of steel balls are used, do following process
Hold the moisture meter vertical so that material in the cup falls in chamber / pressure vessel. Now holding unit horizontally, rotate it for 10 seconds, so that the balls rolled round the inside circumference of pressure vessel. Rest for 20 seconds and repeat the rotation rest cycle until the gauge reading is constant (this usually takes 4 to 8 minutes)
Once you got the percentage of water / moisture available in wet sample of soil, it’s time to calculate the moisture/ water content in dry soil.
For calculating it do following
e = [m / (100 – m)] x 100
where,
m = Percentage moisture of wet mass of soil (result got from moisture meter)
e = moisture content in dry mass of soil as a percentage.
This gives you the moisture content of soil, from which you can calculate the dry density of soil and instruct team to either proceed for further work or repeat compaction on strata again.
You can also get detailed process from IS 2720 part 2.
You might be aware about formula for dry density;
Dry density = bulk density / (1 + e)
When we want a dry density of soil which are compacted in place, first thing we need to know is current moisture / water content in compacted earth.
We relate the achieved density of soil directly with the moisture / water content in it by comparing with its Maximum Dry Density and Optimum Moisture content.
When we send the sample of soil in lab for determination of MDD and OMC, they do test it with different combination of moisture in proctor test and plot a graph which shows the behavior of soil under different moisture levels. From this graph we get the optimum level of moisture at which the soil can attain maximum dry density.
Once we know the properties of soil, it’s very easy to calculate the dry density of soil by relating it to optimum moisture content.
Calculation of dry density of soil involves measuring of its bulk density and finding moisture content of it. There are many methods available for determination of moisture content in soil.
By oven drying – it takes minimum 24 hours and results are very accurate and precise. Due to time it takes, its avoided in places where quick results are required to progress work at faster rates.
Sand Bath method – Results are not much accurate and required heating of sample.
Alcohol Method – same as sand bath method, need to add Methylated spirit in soil sample and then firing sample to make it dry.
Rapid Moisture test by Infrared lamp and torsion balance – it’s easy to do but required electricity for doing this test, so not feasible in remote places or when site area is big and do not have electricity connection (such as a long road construction).
Rapid Moisture meter – Mostly used at all type of projects and specially in Road constructions, involves less risk and time and produces almost accurate results.
Determination of Moisture content by Rapid moisture meter is easier and requires;
Rapid Moisture Meter

It consists of Pressure gauge, pressure vessel, cup for sample, spherical steel balls, bracket to hold it and handle to fix cup in pressure vessel mouth.
Pressure vessel and cup outer body is made up of aluminium alloy, cup inside is of stainless steel, bracket of copper alloy and handle of mild steel.
Counterpoised balance

It consists of a stand, balance arm to take exactly 6-gram sample, pan to put sample and stirrup to tie the pan on arm.
Rapid Moisture Meter determines the percentage of water in soil mass through the gas pressure created by reaction between calcium carbide and water present in the wet soil sample. This percentage water need to be converted to as water content in dry mass of soil sample.
For doing this test, collect the sample from site, and setup the counterpoised balance correctly. Then add soil sample in pan till the mark on the balance arm lines up with the index mark.
Clean the chamber and cup body with wire brush to ensure its completely clean.

Hold the rapid moisture meter horizontally and gently deposit one level scoopful of calcium carbide halfway inside the chamber. Then lay down the chamber without disturbing it.
Put the weighed sample of soil in cup and keeping cup and chamber horizontal, clamp the cup to chamber.
In case when the sample is bulky, put sample in chamber and calcium carbide in cup.
In case of clayey soils and paste, Place 3 smaller steel balls in cup along with soil sample and large ball in chamber.

After clamping cup to chamber tightly, with pressure gauge on downward (except when steel balls are used) shake the moisture meter up and down vigorously for 5 seconds and quickly turn it up so that moisture gauge is on upward.
Give the tap on moisture meter body to ensure all content falls in the cup.
Hold the rapid moisture meter gauge downward and shake it for 5 seconds, then turn it up with gauge upward and tap.
Hold for one minute and repeat it third time.
Once more invert the moisture meter and shake it up and down to cool the gas.
Turn the moisture meter gauge upward and hold it at chest level, when needle / pointer come to rest without fluctuations, take the reading as a percentage of moisture/ water in wet sample of soil.
In case of steel balls are used, do following process
Hold the moisture meter vertical so that material in the cup falls in chamber / pressure vessel. Now holding unit horizontally, rotate it for 10 seconds, so that the balls rolled round the inside circumference of pressure vessel. Rest for 20 seconds and repeat the rotation rest cycle until the gauge reading is constant (this usually takes 4 to 8 minutes)
Once you got the percentage of water / moisture available in wet sample of soil, it’s time to calculate the moisture/ water content in dry soil.
For calculating it do following
e = [m / (100 – m)] x 100
where,
m = Percentage moisture of wet mass of soil (result got from moisture meter)
e = moisture content in dry mass of soil as a percentage.
This gives you the moisture content of soil, from which you can calculate the dry density of soil and instruct team to either proceed for further work or repeat compaction on strata again.
You can also get detailed process from IS 2720 part 2.
You might be aware about formula for dry density;
Dry density = bulk density / (1 + e)
